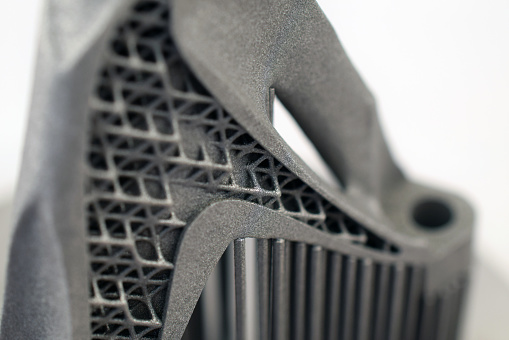
Manufacturing products requires making a component, part, or full item from raw materials. There are two main types of manufacturing processes. One way to make the part involves taking a large chunk of the raw material and cutting, shaving, sawing, or drilling it down until forming the desired shape. This type of process is called subtractive manufacturing. The other type of process involves taking small pieces of the raw material and layering or stacking the pieces on top of each other until forming the item. This manufacturing technique is called additive manufacturing.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing may also be called additive layering manufacturing or 3-D printing. It involves using computer-aided design software (CAD) or a 3-D printing scanner to place down materials layer by layer into the desired geometric shapes. This process was first founded in 1983 and gained momentum in the past decade due to innovation advances. This 3D printing industry had been expected to grow by 31% and generate $21 billion in revenue by 2020, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
The raw material is deposited on the bed using a wide range of technologies based on the materials that are used, how the layers will form, the complexities of the part, and the company’s budget. The material is heated, melted, or cured during the layering process as it then hardens and solidifies as it cools. It creates a strong bond to the previous layer.
While there are many technologies to perform additive manufacturing, there are basically three techniques used by manufacturers. One technique employs the use of ultraviolet light aimed at the materials to cure photopolymer resin in a process called photopolymerization. This technique is called stereolithography.
Another technique involves fully melting the materials. The method to melt the materials may vary, such as using a laser or electron beam. The third technique is to heat the materials without liquefying the materials completely. Heating the materials until they stick together without melting them fully is called sintering.
Types of Additive Manufacturing Processes
There are many types of processes that can be categorized into the three main techniques of sintering, melting, and photopolymerization.
- Material Extrusion: This process involves drawing out long stringers of heated polymers through a nozzle. The materials are layered and adhered to each other through chemical bonding or controlling the temperature.
- Binder Jetting: Binder jetting has a 3-D printer head that deposits the materials in alternating layers. The materials are in powder form as a liquid binder is used to adhere the powder together into the form.
- Sheet Lamination: This process may use ultrasonic welding at low temperatures to join thin metal sheets together. Another method is to use paper materials to layer the materials together using paper and an adhesive.
- Directed Energy Deposition: Directed energy deposition manufacturing utilizes a laser, electron beam gun, or electric arc to build materials on top of each other.
- Directed Energy Deposition-Arc: This technique uses a robotic welding machine to deposit wire using arc welding power. Arc deposition processes can create a range of 3-D geometric shapes.
- Vat Polymerization: Vat polymerization relies on ultraviolet light and mirrors to cure resin from a vat of liquid resin polymer.
- Powder Bed Fusion: This process may use several technologies such as thermal print heads, electron beams, or lasers. The materials are melted or partially melted together to form the component.
Speaking with the manufacturer allows you to decide on the right process and technique that is appropriate for the application. The manufacturer may also provide advice on the which techniques are best based on the chosen material.